

|
Educating future healthcare providers |






|
Medical technologists, also known as clinical laboratory scientists, analyze human blood, tissues and body fluids or supervise the performance of medical laboratory tests using a wide variety of instruments, microscopes, computers, chemicals and other methods of clinical analysis. They perform laboratory tests necessary for the diagnosis and treatment of diseases. |
|
Medical Technology |
|
Nurses provide education to promote health and prevent injury and illness. Nurses' special knowledge and skills are used to monitor patient conditions, give them medications and treatments prescribed by a physician and provide education so that patients can care for themselves at home. |
|
Nursing |
|
Nurse Aides care for patients under the direction of registered nurses, practical nurses and physicians. They assist patients with eating, bathing and other daily activities. Additionally, nurse aides may take vital signs, weights and assist the nursing staff or physician with treatments. |
|
Nurse Aide |
|
The phlebotomist is a major player in the field of laboratory medicine. The diagnosis of a patient is dependent on the quality of blood specimens collected by the phlebotomist. |
|
Phlebotomy |
|
It is the radiographer with the use of digital technology who performs the radiographic examination that creates the images needed for diagnosis. Radiologic Technologists work under the direction of radiologists or other physicians in hospitals, clinics, physician offices and specialized imaging centers. |
|
Radiologial Technology |
|
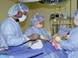
Surgical Technologists are part of a dynamic team which provides patient care before, during and after surgery. Their primary responsibilities are preparing the sterile instrumentation and supplies required for surgical procedures and passing these essentials to the surgeon during surgery. |
|
Surgical Technology |
|
Academic Programs |
|
Carolinas College of health Sciences |